If you are struggling with internal hemorrhoids, you are likely seeking relief and hoping for a solution. Internal hemorrhoids can be difficult to get rid of. They can also be extremely uncomfortable and put you at risk of concerning health issues, such as blood loss or an infection.
Hemorrhoids sometimes go away on their own with a few simple lifestyle changes.
However, that doesn’t mean you should ignore symptoms of internal hemorrhoids and hope for the best.
Knowing when to see a doctor about your symptoms is important if they don’t go away. Seeing an Interventional Radiologist can be valuable because they have an in-depth knowledge of blood vessels and their associated conditions, including hemorrhoids. They specialize in performing minimally invasive procedures that offer a less invasive and often more effective approach to treating hemorrhoids.
If you have internal hemorrhoids, understanding how to manage them effectively and when to consult a doctor is essential. Discover tips for relieving painful hemorrhoid symptoms and when you need to seek professional medical attention.
What Are Internal Hemorrhoids?
Internal hemorrhoids are swollen cushions of veins and other tissue inside the rectum. Unlike external hemorrhoids, which are located outside the rectum, you can’t see or feel internal hemorrhoids.
Internal hemorrhoids are less likely to resolve on their own compared to external hemorrhoids and can lead to more serious symptoms if left untreated. For this reason, most medical treatments for hemorrhoids are designed to target internal hemorrhoids rather than external ones.
Symptoms of Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids aren’t always painful. However, they can cause itching, irritation, and a feeling of pressure in the rectum when you have a bowel movement.
The most common symptom of an internal hemorrhoid is bleeding.1 You may notice blood in the stool or toilet paper after using the bathroom. Minor blood loss from an internal hemorrhoid that goes away isn’t usually a problem, but an untreated hemorrhoid that doesn’t disappear can lead to an increased risk of complications.
When an internal hemorrhoid pushes through to the outside, it’s called a prolapsed hemorrhoid. This type of internal hemorrhoid is visible and, like an external hemorrhoid, can cause pain. Prolapsed hemorrhoids might make it uncomfortable to sit down, especially for extended periods.
If you experience these symptoms, seeking medical advice is important to receive an accurate diagnosis. Early treatment can prevent complications and provide relief from the discomfort associated with hemorrhoids.
Can Untreated Internal Hemorrhoids Disappear?
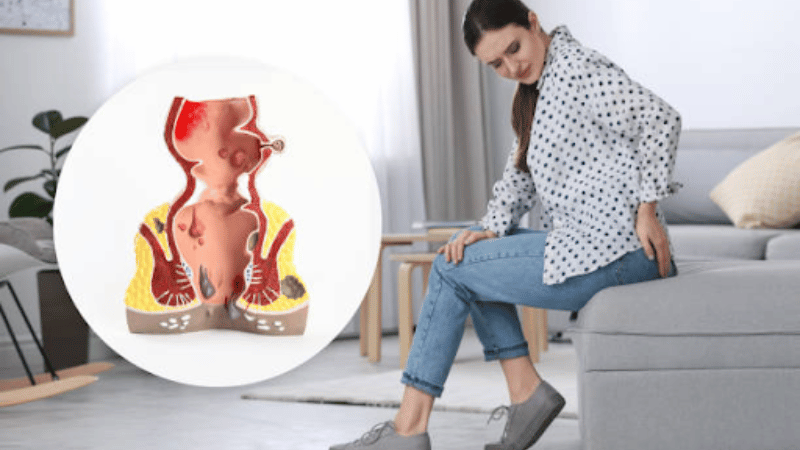

While untreated internal hemorrhoids sometimes resolve, it’s important to resolve symptoms promptly to prevent further complications and ensure proper healing.
Risks of Internal Hemorrhoids
Although Internal hemorrhoids are not immediately dangerous, neglecting them can lead to more severe complications. Here are some of the key risks associated with internal hemorrhoids:
Prolapse
Internal hemorrhoids can prolapse, meaning they extend beyond the anus. This can lead to discomfort and complications, as prolapsed hemorrhoids may become trapped and require medical intervention.
Strangulation
In some cases, the blood supply to a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid can be cut off by the anal muscles, leading to strangulation. This condition can cause severe pain and may result in tissue death if not treated promptly.
Thrombosis
Internal hemorrhoids can develop blood clots, leading to thrombosed hemorrhoids. This can cause significant pain and swelling and may require surgical intervention.
Infection
If internal hemorrhoids become prolapsed and collect mucus or stool particles, they can lead to irritation and infection. This can result in conditions such as pruritus ani (itching around the anus)
Bleeding
Internal hemorrhoids can cause bright red bleeding during bowel movements. While this is often not life-threatening, it can be alarming and may indicate more serious conditions, such as colorectal cancer, necessitating further investigation.
Chronic Discomfort
Persistent symptoms such as pain, itching, and discomfort can significantly affect quality of life and lead to avoidance of certain activities, including exercise and social engagements.
Straining
Individuals with internal hemorrhoids may experience increased straining during bowel movements, which can exacerbate the condition and lead to further complications, including worsening hemorrhoids or the development of anal fissures.
When Should You See a Doctor About Hemorrhoid Symptoms?

If internal hemorrhoid symptoms don’t go away after a week or accompany other symptoms, such as bleeding, it’s a good idea to have an experienced hemorrhoid specialist evaluate your symptoms.
See a doctor immediately if you notice severe symptoms, such as dark red blood, severe pain, or more than a small amount of blood loss. These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious health issue, such as colorectal or anal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or large anal fissures.
Treatments for Internal Hemorrhoids
When internal hemorrhoid symptoms persist or worsen, treatment may be necessary to alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications. Depending on the severity, various treatment options are available, from non-invasive approaches to surgical procedures. Here are some of the most common treatments:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Creams and ointments that reduce inflammation and ease discomfort.
- Rubber Band Ligation: A minimally invasive procedure where a band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off blood flow.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
- Coagulation Therapy: Laser or infrared light hardens and shrinks the hemorrhoid.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: A surgical procedure to completely remove large or prolapsed hemorrhoids.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: This surgery repositions the hemorrhoids and reduces blood flow, causing them to shrink.
- Hemorrhoidal Artery Embolization (HAE): A non-surgical procedure that blocks blood flow to the hemorrhoidal arteries, causing the hemorrhoids to shrink.
Hemorrhoidal Artery Embolization (HAE) for Internal Hemorrhoids
If a conservative approach isn’t relieving symptoms, a more advanced hemorrhoid treatment should be considered to address internal hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoidal artery embolization (HAE) is a non-surgical treatment for internal hemorrhoids. It offers fast relief from bleeding and other symptoms and is extremely safe. Studies have found no serious complications after hemorrhoid embolization.2
Most people with internal hemorrhoids that won’t go away can benefit from HAE. It’s less invasive than surgery and doesn’t cause rectal wounds or issues with anal incontinence. Other treatment options include infrared coagulation, rubber band ligation, and hemorrhoid surgery.
Why Choose USA Hemorrhoid Centers
USA Hemorrhoid Centers is a trusted national network of specialized, non-surgical hemorrhoid treatment centers dedicated to providing effective relief. Our experienced team of hemorrhoid doctors tailors treatments to each individual’s needs, ensuring a personalized and comfortable experience.
Our hemorrhoid specialists are experts in hemorrhoidal artery embolization and are committed to helping patients return to their daily lives free of hemorrhoid symptoms and discomfort.
We also accept most types of insurance and offer affordable payment plans so you can focus on your health without financial stress.
If you’re concerned about hemorrhoid symptoms, schedule a consultation at a clinic near you today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do internal hemorrhoids last?
There is no set timeline for hemorrhoids. They can go away in a few days or last for months or years. Some people have recurring hemorrhoids, so it seems like their symptoms never go away.
If internal hemorrhoid symptoms don’t clear up after a week, schedule an appointment with a hemorrhoid doctor for an evaluation.
What are the risks of untreated hemorrhoids?
If a clot forms in the hemorrhoid, it can burst, causing serious blood loss and requiring immediate medical attention.
Blood loss that’s dark red or excessive could also indicate a more serious health condition. Rectal bleeding is a symptom of many different conditions, including hemorrhoids, anal fissures, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer, so it’s important to see a hemorrhoid doctor for an evaluation if you notice regular blood in your stool.
Untreated internal hemorrhoids can also cause anal tears, which can become infected.
Why do internal hemorrhoids need treatment?
If left untreated for too long, hemorrhoids can push out of the rectum and become prolapsed. These hemorrhoids can be painful and make everyday life more uncomfortable. There’s also a risk of blood loss, infection, and a blood clot if an internal hemorrhoid is left untreated for too long.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of hemorrhoids. Early treatment can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Are internal hemorrhoids permanent?
Internal hemorrhoids aren’t permanent. There are safe and effective treatments that will make even severe internal hemorrhoids go away.
References:
- Sun, Z., & Migaly, J. (2016). Review of Hemorrhoid Disease: Presentation and Management. Clinics in colon and rectal surgery, 29(1), 22–29.
- Reza Talaie,, Pooya Torkian, et all. Hemorrhoid embolization: A review of current evidences. Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging. Volume 103, Issue 1, January 2022, Pages 3-11