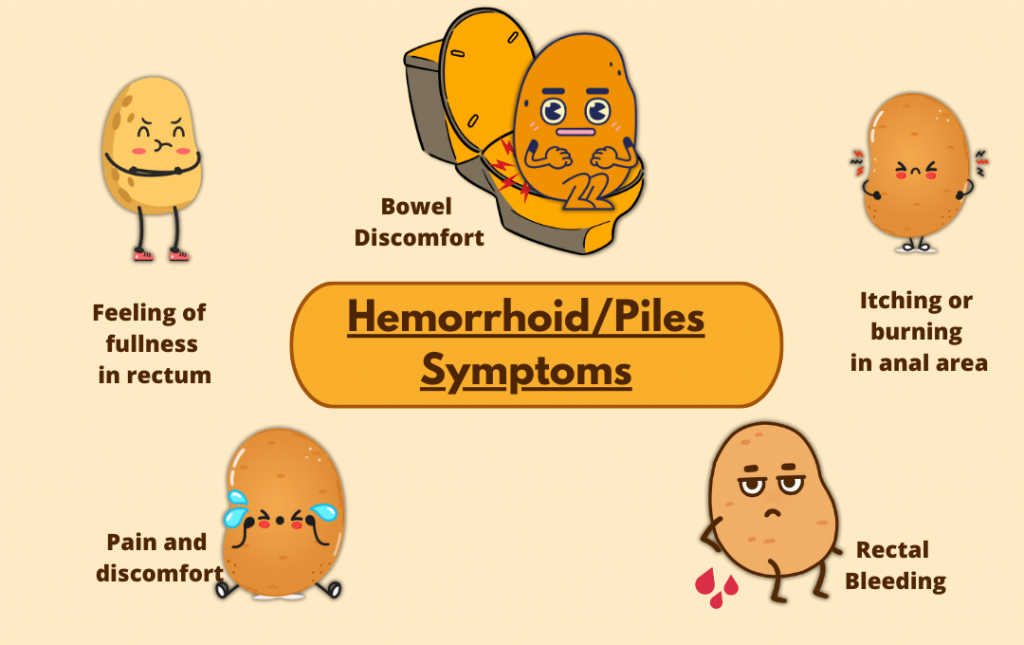
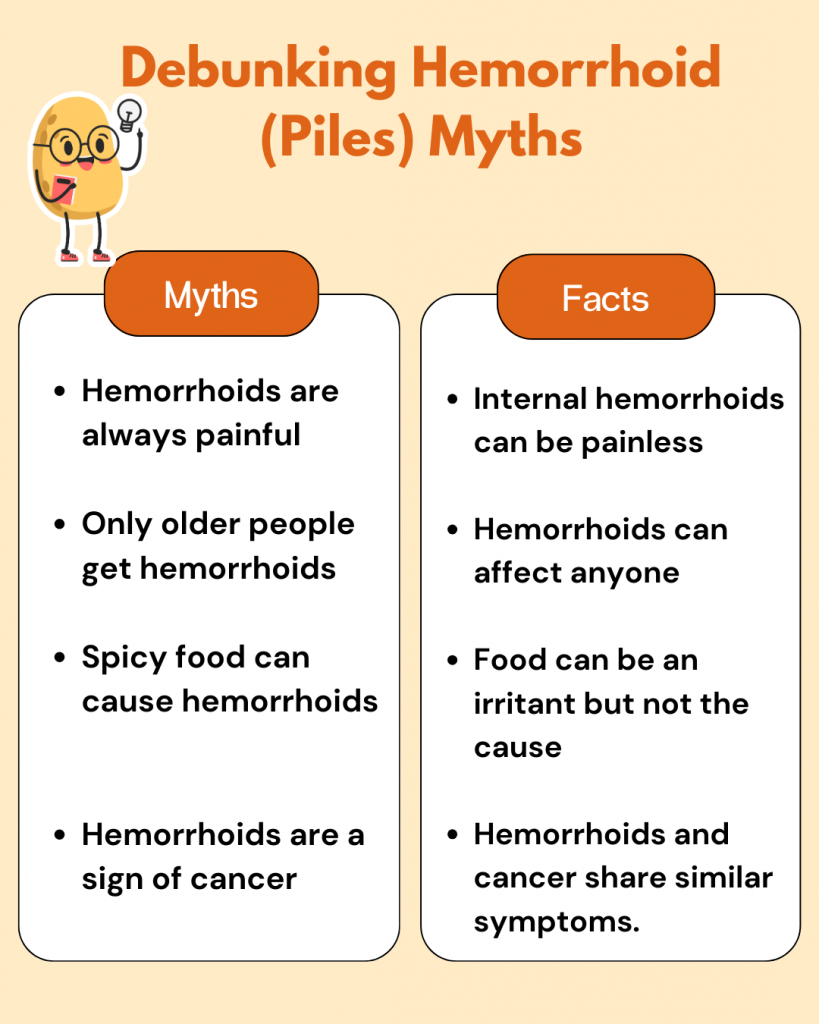
Hemorrhoids typically last from a few days to several weeks. However, some internal hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins located inside the rectum, won’t heal on their own. They require medical treatment to help the hemorrhoid tissue shrink, and they can become increasingly severe if left untreated.
These persistent hemorrhoids can cause painful symptoms, including anal itching, blood in the stool, and bowel discomfort. If they become prolapsed, meaning they fall outside of the anus, they can also be intensely painful. Ongoing hemorrhoid symptoms can impact the quality of your everyday life. Additionally, the longer you have internal hemorrhoids, the greater the risk of complications, so it’s important to know when to see a doctor because of hemorrhoids.
Types of Hemorrhoids and Their Duration
Knowing how to recognize symptoms for different types of hemorrhoids and what to expect in terms of duration can help you determine when to see a doctor.
How Long Do Internal Hemorrhoids Last?
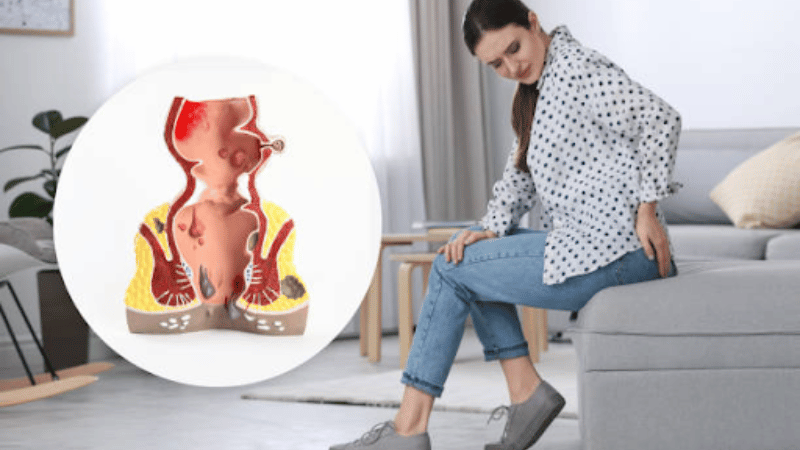
Internal hemorrhoids usually sit inside the rectum and can vary in their duration. The duration depends on a few factors, such as whether the person experiences symptoms because internal hemorrhoids can be asymptomatic. When an internal hemorrhoid prolapses, patients may notice symptoms that can intensify, including anal itching, irritation, discomfort, and blood in the stool or on toilet paper. Other factors such as constipation, diarrhea, pregnancy, age, and weight can also impact the duration of the internal hemorrhoid. If the internal hemorrhoid doesn’t go away within a week or so, patients should consider getting medical treatment for their hemorrhoid.
If an internal hemorrhoid is large enough to cause symptoms, such as blood in the toilet bowl or on toilet paper after a bowel movement, anal itching, irritation, and discomfort, it may last several weeks or more. An internal hemorrhoid that prolapses or causes severe symptoms might persist until it’s treated.
How Long Do External Hemorrhoids Last?
External hemorrhoids, which are hard, tender lumps around the anus, can often last a few days; however, they may take longer to resolve. This depends on the size of the external hemorrhoid and other factors that may prolong its time frame, such as friction from wiping. Generally, over-the-counter medications and at-home treatments can help alleviate or reduce symptoms.
How Long Do Thrombosed Hemorrhoids Last?
A thrombosed hemorrhoid can last for two to three weeks or longer. A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when an external or internal hemorrhoid fills with one or more blood clots. They can be very painful and swollen, impacting walking, sitting, or passing a stool.
Sometimes, the blood clots diminish in a couple of weeks, but the hemorrhoid doesn’t necessarily go away. If there’s too much pressure, a thrombosed hemorrhoid can rupture. A ruptured hemorrhoid can cause intense pain and bleeding. It can also increase your risk of infection, especially if the thrombosed hemorrhoid is external.
Factors That Affect Internal Hemorrhoid Healing

An internal hemorrhoid that doesn’t heal within a week or two should be seen by a specialist. But, what factors impact how quickly an internal hemorrhoid heals?
- Severity of the hemorrhoid. If an internal hemorrhoid is very swollen and enlarged, it’s more likely to prolapse or cause more persistent symptoms that require treatment. Typically, grade-1 hemorrhoids are most likely to heal on their own. Later-stage hemorrhoids are more likely to require medical treatment.
- Lifestyle factors. Eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and being physically active can promote faster healing.
- Underlying health conditions that may prolong symptoms. Being overweight or pregnant can put pressure on the rectum, making it harder for hemorrhoids to heal. Constipation also puts pressure on the veins in the lower rectum and anus, which can cause hemorrhoids and lead to worsening symptoms and slower healing.
If your hemorrhoids aren’t healing or if symptoms persist, it may be time to consider a more advanced solution. USA Hemorrhoid Centers offers a modern treatment for internal hemorrhoids that has fewer risks and a shorter recovery than hemorrhoid surgery. Hemorrhoid artery embolization (HAE) is a good option for most cases of internal hemorrhoids that don’t go away on their own.
HAE: A Minimally Invasive, Long-Term Solution
Hemorrhoid artery embolization (HAE) is a non-surgical treatment for internal hemorrhoids. It targets the blood flow causing the hemorrhoids, helping to reduce inflammation, swelling, and other symptoms, and has been proven to provide effective, long-term relief. HAE has a 97% clinical success rate.
The benefits of choosing HAE over traditional treatment surgical methods are that it doesn’t involve removing or cutting any tissue. The procedure isn’t painful, and there’s less risk of bleeding or an infection. HAE can be performed in an outpatient setting, and most people can return to their normal activity levels within a few days.
When to See a Doctor for Hemorrhoids

If you notice internal hemorrhoid symptoms for more than a week or two, or if the hemorrhoid prolapses and becomes painful, it’s important to see a hemorrhoid doctor. You should see a doctor if you notice signs of an infection, such as intense swelling or a fever.
You can try over-the-counter hemorrhoid treatments, such as a cream or suppository, to relieve the swelling and inflammation. At-home care, such as soaking in a sitz bath (a shallow bath) and ice packs, can also bring relief. Additionally, avoiding prolonged sitting for long periods, adding fiber to the diet, drinking enough water, and exercising can support healing. If there is blood in the stool, anal itching, and other internal hemorrhoid symptoms persist after a week or two despite home care methods, schedule a consultation so you can get the treatment you need for lasting relief.
FAQs
How long do hemorrhoids last if untreated?
There is no set duration for how long hemorrhoids last. External hemorrhoids generally go away eventually without treatment, although they can last several weeks or longer. Internal hemorrhoids generally last longer than external hemorrhoids, but can cause chronic symptoms that may need medical treatment.
Can hemorrhoids come back after treatment?
Yes, hemorrhoids can come back after treatment. Addressing risk factors for hemorrhoids, such as constipation, being sedentary, and eating a low-fiber diet, can help reduce the chances of hemorrhoids returning.
Is it bad to have hemorrhoids for long periods of time?
Hemorrhoids themselves aren’t dangerous. However, having hemorrhoids for long periods increases your risk for developing more severe symptoms or complications, such as an infection or severe pain and bleeding from a thrombosed hemorrhoid that ruptures.