Can prolonged sitting, which is uncomfortable for many people, also lead to hemorrhoids?
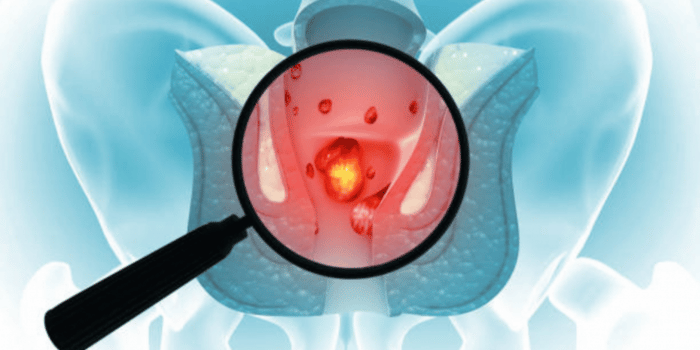
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or rectum. Prolonged sitting can contribute to hemorrhoids or worsen existing ones by causing anal veins to lose elasticity and become swollen. Factors such as how long you sit and the type of surface impact how prone anal veins are to swelling and inflammation.
Hemorrhoids are preventable, so even people who tend to sit for long periods for work or travel can avoid these issues. They’re also treatable with non-surgical options, offering long-term relief from discomfort, pain while sitting, and other symptoms.
Can Sitting Make Hemorrhoids Worse?
Yes, sitting for a long time puts extra pressure on the blood vessels in your bottom and slows the blood moving in and out of that area. This makes it harder for any existing hemorrhoids to get better and increases the chances of them getting bigger or causing more problems.
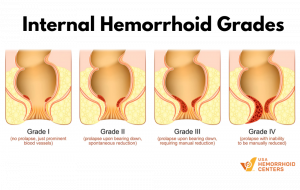
Prolonged sitting can become increasingly painful if internal hemorrhoids are prolapsed, meaning they’ve become severe enough to slip outside of the anus and don’t return to their original position on their own.
Hemorrhoids can also take longer to heal with long periods of sitting. The extra pressure on the veins and reduced blood flow mean slower healing and a higher risk that the hemorrhoids will progress.
VIEW OTHER HEMORRHOID SYMPTOMS
How Prolonged Sitting Impacts Hemorrhoid Development

Sitting for long periods, whether at work, during travel, while on the toilet, or for another reason, is a risk factor for hemorrhoid development. There’s pressure on the rectal area when sitting, which can be worse on a hard surface or with poor posture. Circulation also slows down, impacting the flow of blood to rectal and anal veins.
Increased Pressure on Rectal Veins
When sitting, the muscles of the buttocks region spread out, which causes rectal and anal veins to stretch. These veins have less elasticity, making them more fragile and likely to swell.
Reduced Circulation While Sitting
Slower circulation to the pelvic region when sitting can cause blood to pool, filling the already stretched veins with blood and leading to swelling and inflammation.
Poor Posture on the Toilet
Poor posture while on the toilet can also play a role in hemorrhoid development. When sitting with the feet flat on the floor and the back straight, the rectum is constrained, increasing pressure on the veins. Putting the feet on a stool so the knees are raised can relax the rectum, helping to protect the veins from excessive pressure.
CAUSES OF INTERNAL HEMORRHOIDS
Can Sitting on the Toilet Too Long Cause Hemorrhoids?
Sitting on the toilet for too long due to constipation can cause hemorrhoids or make existing ones worse. While on the toilet, the rectum is lower than the rest of the buttocks, which causes gravity to push on the veins and blood to pool. Pressure from straining during a bowel movement can cause the veins to swell.
Here are some tips to help reduce bowel-related strain:
- Limit toilet time to under 5 minutes.
- Don’t use phones or read in the bathroom.
- Avoid forcing a bowel movement. Get up and try again later if you’re constipated.
How to Prevent Hemorrhoids if You Sit All Day

If you sit a lot, there are steps you can take to help prevent hemorrhoids.
- Take regular breaks from sitting: Stand up or walk around every 30 to 60 minutes to help increase blood flow and reduce the pressure on the anal and rectal veins.
- Use a cushioned seat: If you normally sit in a hard chair at work, consider sitting on a special cushion to help prevent hemorrhoids. A hemorrhoid cushion supports the perineum and elevates the legs to reduce pressure on the rectum.
- Maintain good posture: Keep your back straight instead of slouching. Slouching can put more pressure on the anal area.
- Stay hydrated and eat plenty of fiber: Staying hydrated and adding fiber to your diet can help prevent constipation. Constipation is one reason people end up sitting for longer on the toilet. Straining because of constipation can also cause hemorrhoids.
- Exercise regularly: Staying active improves blood circulation and reduces the impact of prolonged sitting. Walking, swimming, yoga, tennis, and dancing are all great activities to help prevent hemorrhoids.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids from Sitting
If hemorrhoids persist for more than a few days or worsen, procedures like hemorrhoid artery embolization (HAE) can offer relief. HAE is a non-surgical procedure performed by an interventional radiologist. It targets the root cause of hemorrhoids by reducing blood flow to the swollen veins, causing them to shrink.
HAE is a low-risk, painless procedure with a short recovery time, and it’s a good treatment option for hemorrhoids that don’t heal on their own.
Get Relief and Prevent Future Hemorrhoids
It is possible for hemorrhoids to develop from sitting too much. Prolonged sitting can also worsen hemorrhoids or slow healing.
Making lifestyle changes to reduce sitting time, prevent constipation, and relieve pressure on anal and rectal veins can help prevent hemorrhoids from developing and ease the pain and discomfort caused by existing hemorrhoids. If hemorrhoid symptoms interfere with your daily life or persist, however, it’s important to see a hemorrhoid doctor for treatment.
USA Hemorrhoid Centers is America’s leading network of hemorrhoid treatment centers. Our doctors have expertise in treating hemorrhoids non-surgically with HAE and can create a personalized treatment plan to help you get relief. Find a hemorrhoid center near you to schedule a consultation with one of our expert doctors.
FAQs
How do I know if my sitting habits are causing hemorrhoids?
If you notice hemorrhoid pain when sitting, discomfort, or other symptoms, such as itching or bleeding, you may have hemorrhoids. Your sitting habits might be the cause, or they could make existing hemorrhoids worse by weakening the veins and increasing swelling and inflammation.
Are standing desks better for preventing hemorrhoids?
Standing desks are better than chairs for preventing hemorrhoids because they help you avoid prolonged sitting. There’s less pressure on anal and rectal veins when standing at a desk.
Can exercise help with hemorrhoids caused by sitting?
Yes, exercise can help with hemorrhoids caused by sitting. Physical activity improves circulation and supports better vein health.